Harnessing the Power of SAP ERP
This is custom heading element
SAP ERP, an acronym for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing Enterprise Resource Planning, is a game-changing software developed by the German tech giant, SAP SE. This innovative software is a modular system designed to seamlessly integrate the core functions of an organization’s business processes into a single, unified system. It’s like the central nervous system of a business, connecting various functions and ensuring they work in harmony.
B. A Trip Down Memory Lane: The SAP Story
The SAP journey began in 1972 when five former IBM employees in Mannheim, Germany, decided to create a software that would revolutionize how businesses operate. Their vision was to develop a system that would enable businesses to interact with a common corporate database for a comprehensive range of applications in real time. Today, SAP stands as a testament to their vision, transforming businesses across the globe.
Decoding SAP ERP
A. The Role of ERP in Streamlining Business Processes
SAP’s suite of ERP products empowers businesses to streamline their processes, including accounting, sales, production, HR, and finance, in an integrated environment. The data from each module is stored in a central database, eliminating data silos and ensuring seamless information flow across the organization.

B. The Building Blocks of SAP ERP: The Modules
SAP ERP is like a Lego set, comprising various modules, each focusing on an essential business function. These modules, ranging from finance and accounting to HR, production, materials management, and customer relationship management (CRM), can be customized to fit the unique needs of each business.
C. The Evolution of SAP: From ECC to S/4HANA
SAP ECC, an on-premises ERP system, has been the backbone of many medium and large companies. However, with the advent of S/4HANA in 2015, SAP took a giant leap forward. S/4HANA is an in-memory ERP platform optimized for the SAP HANA in-memory database platform, designed to reduce complexity and pave the way for intelligent enterprises.
III. The SAP Advantage: Features and Benefits
A. Standardization: The First Step to Efficiency
One of the standout advantages of SAP ERP is the standardization of an organization’s business processes. By creating a common language and process flow, SAP ERP eliminates inefficiencies and reduces the scope for errors.
C. Customizability: One Size Does Not Fit All
Every business is unique, and SAP ERP acknowledges this fact. Its high degree of customizability allows organizations to tailor the system to their specific needs, ensuring a perfect fit.
B. A Unified View: The Big Picture
SAP ERP provides a unified view of the business, breaking down departmental silos and fostering cross-functional collaboration. This holistic view helps enforce financial, process, and legal controls, ensuring compliance and risk mitigation.
D. Data-Driven Decision Making
With its robust reporting and analytics features, SAP ERP turns data into actionable insights, aiding in informed decision-making. It’s like having a crystal ball that provides a glimpse into the future, enabling businesses to stay one step ahead.
IV. Implementing SAP ERP: A Reality Check
A. The Investment: Time and Money
Implementing SAP ERP is a significant investment. It involves not just the cost of purchasing the software and the underlying infrastructure, but also the labor costs of internal IT employees and external consultants, training expenses, and ongoing costs of software maintenance and upgrades.
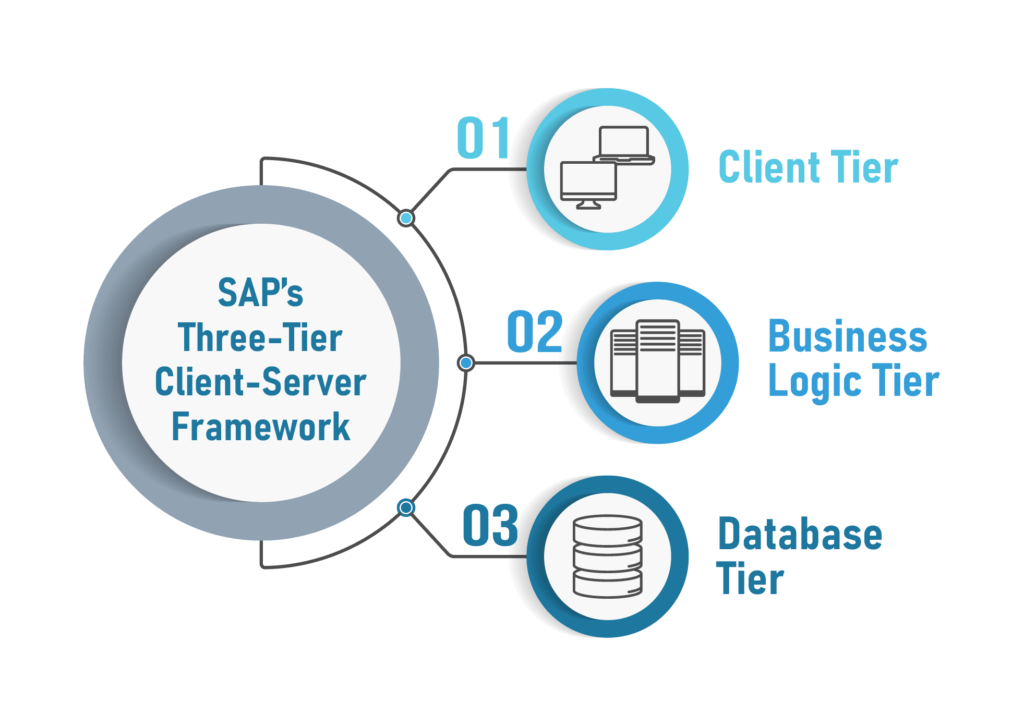
B. The Complexity: A Double-Edged Sword
The complexity of the SAP ERP system, while being its strength, is also a challenge. Implementations can take several years, requiring meticulous planning and execution.
C. The Implementation Timeline: A Marathon, Not a Sprint
Implementing SAP ERP is not a sprint; it’s a marathon. It involves a significant timeline and can present various challenges, from the need for extensive training to managing the change within the organization.
V. Industry-Specific Functionality: A Closer Look
A. SAP ERP: A Jack of All Trades
SAP ERP is not a one-trick pony. It includes a broad range of business applications and offers industry-specific functionality, making it a versatile solution for businesses across sectors.
B. Real-World Applications
From finance to HR, procurement, and logistics, ERP software helps organizations manage nearly every aspect of their business. Its industry-specific applications further enhance its relevance, making it a preferred choice for businesses worldwide.
VI. The Future of SAP ERP: The Road Ahead
A. SAP HANA: The Next-Gen Platform
SAP HANA is an in-memory database platform that allows for processing high volumes of data in real-time. It’s the engine that powers the next generation of SAP ERP systems, enabling businesses to operate in real-time.
B. The Cloud Advantage
SAP is increasingly focusing on cloud-based solutions, recognizing the scalability, flexibility, and cost advantages that the cloud offers.
C. SAP Business ByDesign and SAP Business One: The New Kids on the Block
SAP Business ByDesign and SAP Business One are the new entrants in the SAP family. While Business ByDesign is a SaaS ERP system targeted at the midmarket segment, Business One is designed for smaller businesses and can run on-premises or in the cloud.
VII. Conclusion
A. Key Takeaways
SAP ERP is more than just a software; it’s a catalyst for business transformation. By integrating various business processes, providing a unified view of the business, and offering robust reporting and analytics features, SAP ERP drives business efficiency.
B. The Bottom Line
In a world where change is the only constant, SAP ERP equips businesses with the tools to not just survive but thrive. It’s not just about doing things differently; it’s about doing different things. And that’s the SAP advantage.
FAQ Section
What is SAP ERP?
SAP ERP is a modular software designed to integrate the main functions of an organization’s core business processes into a unified system.
What are the benefits of SAP ERP?
SAP ERP offers several benefits, including the standardization of business processes, a unified view of the business, customizability, and robust reporting and analytics features.
What is the difference between SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA?
SAP ECC is an on-premises ERP system, while S/4HANA is an in-memory ERP platform optimized for the SAP HANA in-memory database platform.
What are the challenges of implementing SAP ERP?
Implementing SAP ERP involves high purchase and implementation costs and can be complex, meaning implementations can take several years.
What is the future of SAP ERP?
The future of SAP ERP includes a focus on cloud-based solutions and the introduction of systems like SAP HANA, SAP Business ByDesign, and SAP Business One.












Leave a Reply